How Does Shazam “Know” That Song? A Look at Audio Fingerprinting in MATLAB
Have you ever been in a coffee shop, heard a song, and used an app like Shazam to instantly identify it? That “magic” is a brilliant piece of technology called audio fingerprinting, and a fascinating repository by Chris Sunny, Audio_finger_printing_using_matlab, shows us how to build this system from the ground up.
This project is a deep dive into the signal processing that makes song recognition possible, all implemented in the powerful engineering environment, MATLAB.
What Is Audio Fingerprinting?
An audio fingerprint is a small, unique digital signature for an audio file. Unlike a hash (like an MD5 or SHA-1), a fingerprint is “fuzzy.” This means it can identify a song even if it’s:
- Playing in a noisy room.
- Recorded on a low-quality microphone.
- Only a small 10-15 second snippet.
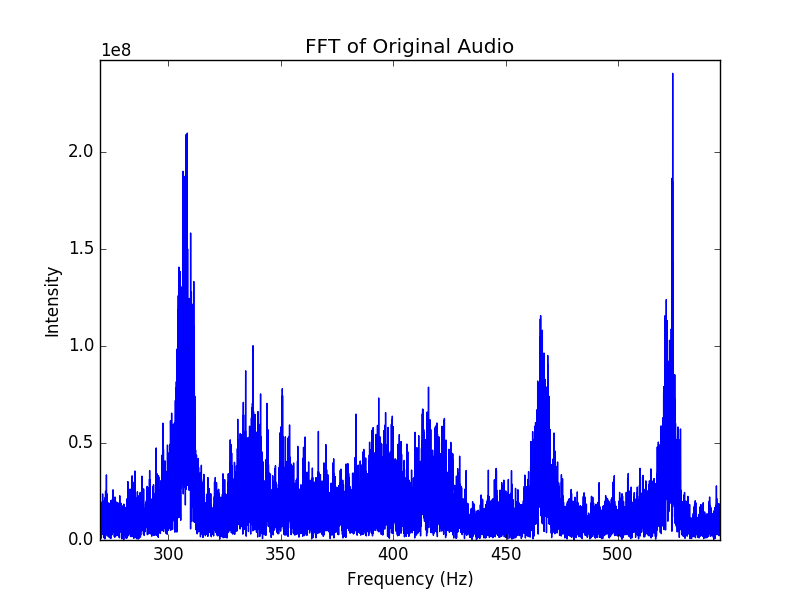
The algorithm works by analyzing the audio’s spectrogram—a visual map of the sound’s frequencies over time. It identifies “peaks” or other robust features in this map and turns them into a unique set of data points. This is the song’s “fingerprint.”
[Image of an audio spectrogram]
How This MATLAB Project Works
This repository contains all the key components for a complete, end-to-end song recognition system. Based on the file names, the project is split into three main parts:
DatabaseCreatorFinal.m(Creating the Database): This script is the “librarian.” You would feed it a folder of your known songs (e.g., your MP3 library). It runs theFINGERPRINT.malgorithm on every song and stores the unique fingerprints in a database (likely the.csvfiles).FINGERPRINT.m(The Core Algorithm): This is the secret sauce. This MATLAB file contains the code that reads an audio file, analyzes its spectral features (as seen inspectralanalysis.mandSpectrogram.m), and generates the unique fingerprint.MAtchCodeFinal.m(Finding the Match): This is the “Shazam” part. This script takes a new, unknown audio sample, generates its fingerprint on the fly, and then searches the database for the closest match.
Why MATLAB?
MATLAB (MATrix LABoratory) is a perfect choice for this kind of work. It’s built from the ground up for high-level mathematics and signal processing. Its powerful built-in functions for audio analysis, spectrograms, and matrix math make it ideal for prototyping and testing complex algorithms like this one.
Even better, the repository includes a GUI.fig file, which means the author built a Graphical User Interface in MATLAB, allowing a user to simply click a button to load a test song and identify it without having to run complex commands.
For any student or enthusiast of digital signal processing (DSP), this repository is a treasure. It’s a hands-on, practical implementation of one of the most widely used and impressive audio technologies in the modern world.
Python code
Check out the Audio_finger_printing_using_matlab project on GitHub here!
