LiDAR Perception Methods Comparison
LiDAR perception is a critical part of autonomous driving and robotics. Various architectures exist for 3D object detection and scene understanding from LiDAR point clouds. Below is a comparison of popular methods.
1. 3D CNN
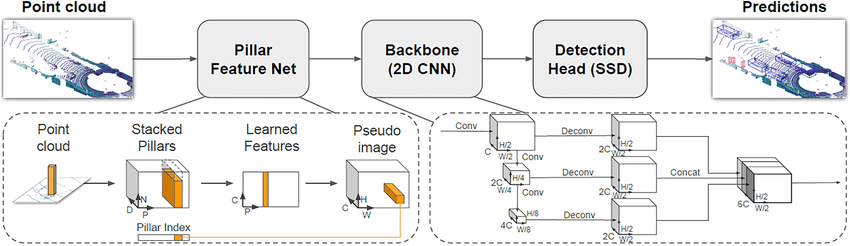
2. PointPillar
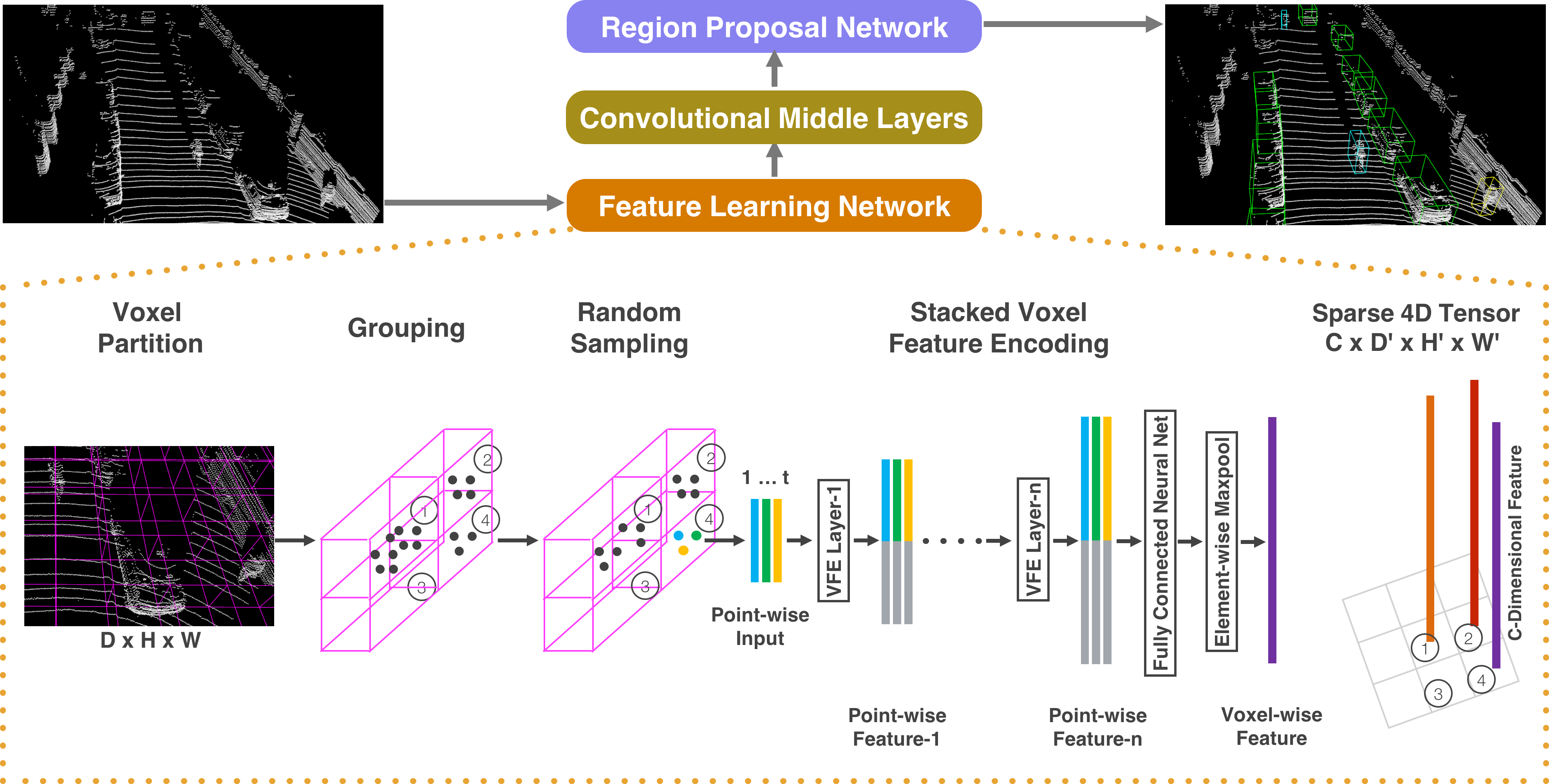
3. VoxelNet
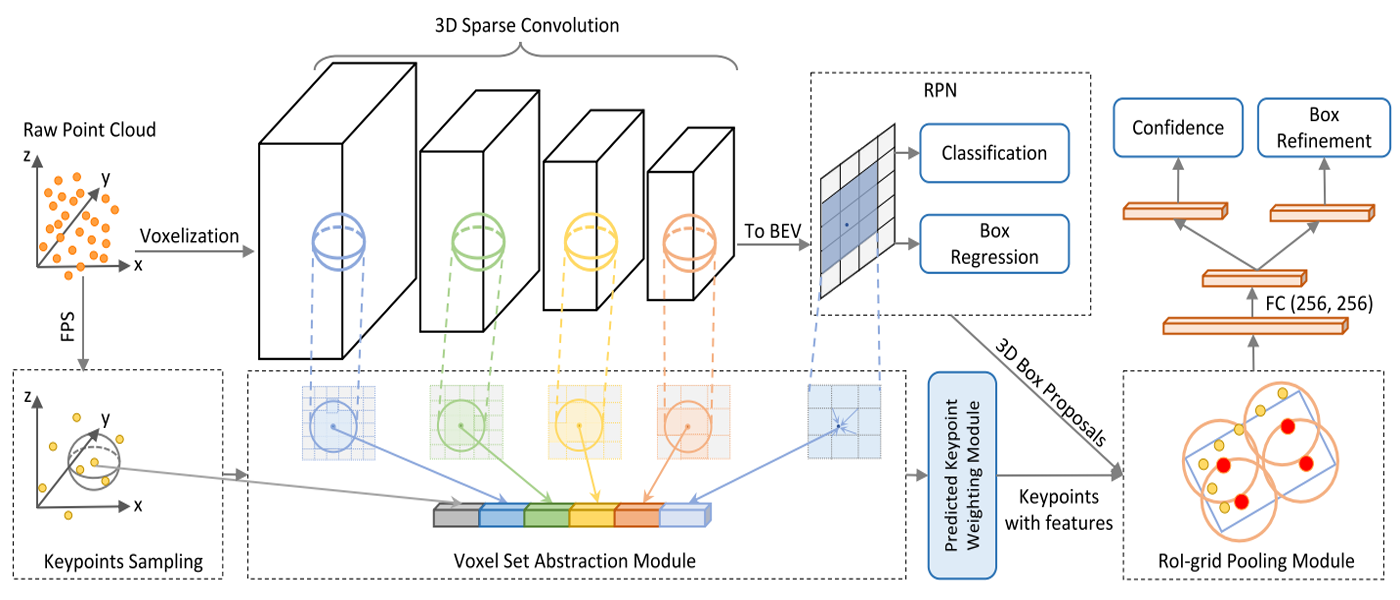
4. PV-RCNN
5. CenterPoint
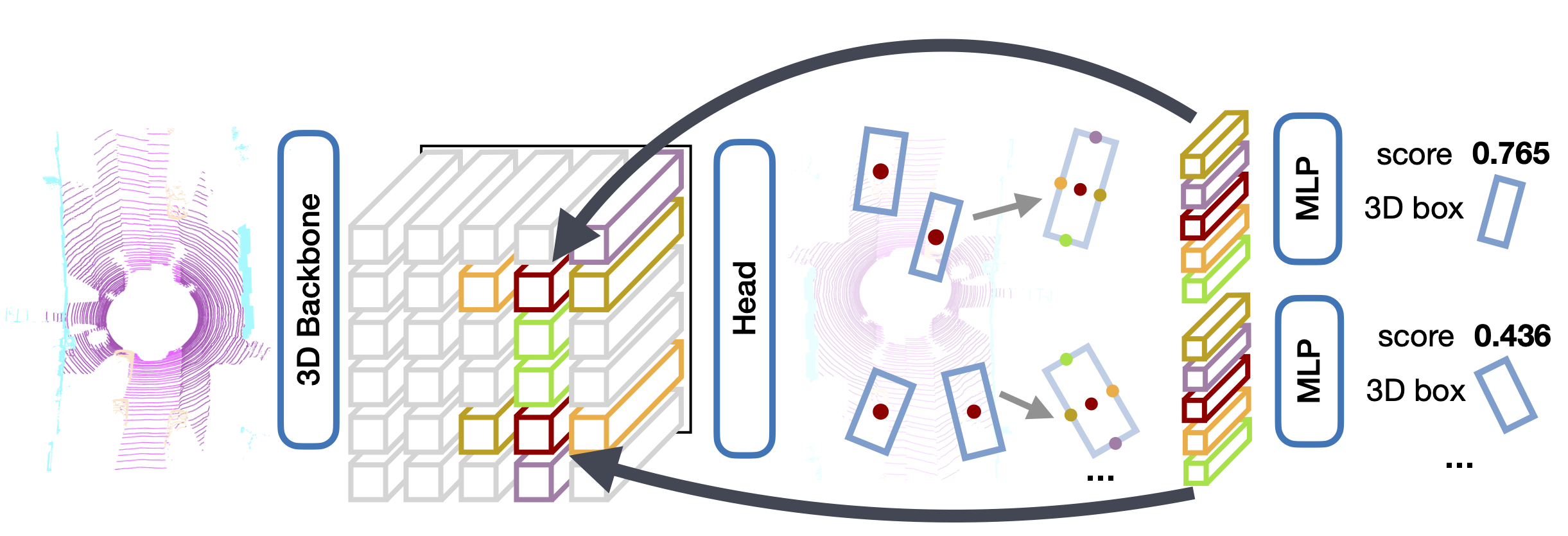
| Method | Input Representation | Network Type | Pros | Cons | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D CNN | 3D voxel grid | 3D Convolutions | High spatial accuracy, full 3D context | Very computationally expensive | Dense LiDAR scenes, high precision detection |
| PointPillar | Point clouds → pseudo-image | 2D CNN (pillars) | Lightweight, fast, good accuracy | Loses some fine 3D details | Real-time autonomous driving |
| VoxelNet | 3D voxel grid | 3D CNN + RPN | Accurate, end-to-end learning | Heavy compute, memory-intensive | High-resolution 3D detection |
| MMDetection3D | Supports voxel, point, and BEV | Modular 3D networks | Flexible, supports multiple backbones | Requires configuration and tuning | Research, multi-dataset experiments |
| SECOND | Sparse voxel grid | Sparse 3D CNN | Efficient, fast, memory-saving | Requires sparse convolution support | Real-time detection |
| PV-RCNN | Point + voxel fusion | Hybrid (3D CNN + PointNet) | High accuracy, retains point-level info | More complex architecture | State-of-the-art LiDAR detection |
| CenterPoint | Point cloud / voxel | Anchor-free detection | Accurate center-based detection | High training complexity | Autonomous driving, tracking |
| BEV Detection | Bird’s Eye View (2D projection) | 2D CNN / Transformer | Efficient, good horizontal coverage | Limited vertical info | Autonomous driving, traffic planning |
| BEV Fusion | Multi-modal BEV | 2D CNN + fusion | Robust, handles occlusion and multi-sensor | Complex, high compute | High-level autonomous perception |
Key Notes:
- Voxel-based methods (3D CNN, VoxelNet): Great for accuracy but heavy on computation.
- Point-based methods (PointPillar, PV-RCNN): Efficient and retain fine-grained 3D details.
- BEV methods: Simplify 3D perception into 2D space for efficiency and multi-modal fusion.
- MMDetection3D: A flexible research framework supporting many of these approaches.
This table provides a quick overview to help choose the right LiDAR perception architecture depending on accuracy, efficiency, and use case.