Temporal Networks
How to deal with temporal information in machine learning
Graph Convolution Networks (GCNs) for Temporal Data
Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) have become essential in handling temporal data, particularly in applications such as human pose estimation and spatio-temporal feature extraction. By combining the ability to capture both spatial and temporal dependencies, GCNs enable powerful modeling of dynamic data over time.
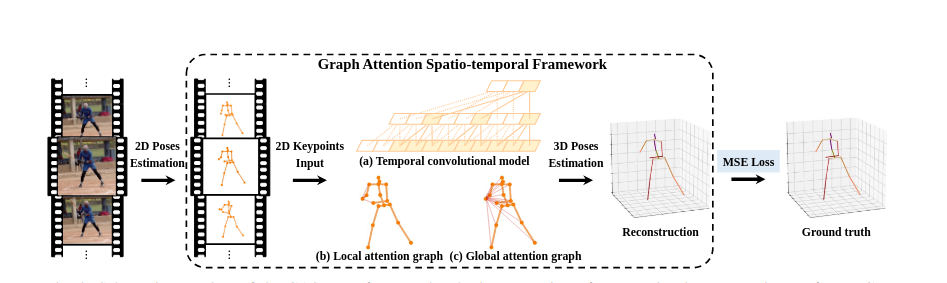
The Graph Attention Block is crucial in effectively expressing the hierarchical and symmetrical structure of human poses, allowing for adaptive extraction of global semantic information over time. By focusing on both local and global spatial blocks interleaved with temporal blocks, GCNs can fuse spatio-temporal features from sequences of 2D keypoints, enhancing the learning of temporal dynamics in video data or sequential data from sensors.
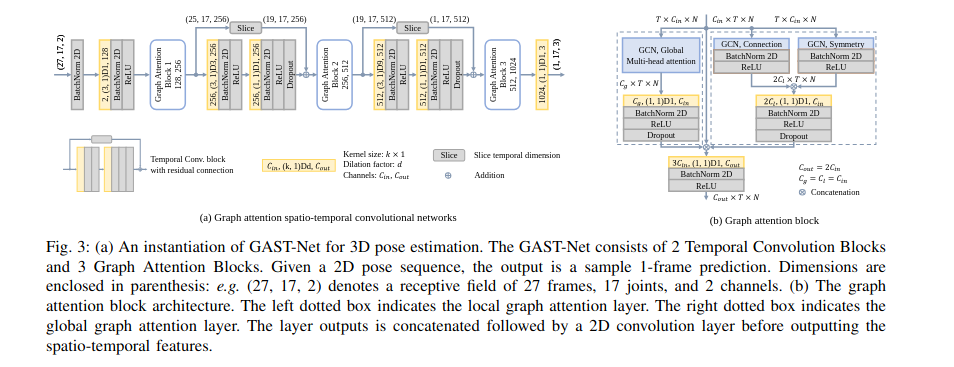
Video Demonstration
The ability of GCNs to adaptively fuse spatial and temporal features makes them ideal for tasks such as human pose tracking, motion recognition, and other time-series predictions.
Vision Transformers (ViTs)
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have gained popularity for their effectiveness in processing spatial-temporal information. Unlike traditional CNNs, ViTs treat image patches as sequences, enabling them to capture long-range dependencies and perform well in tasks like video classification and sequence modeling.
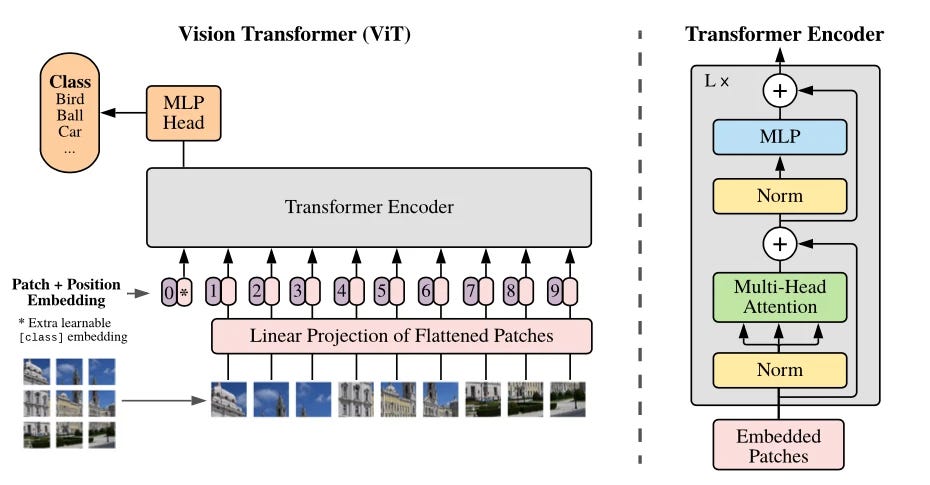
ViTs have shown significant success in integrating temporal dynamics, offering a new approach to handling video data compared to CNN-based architectures.
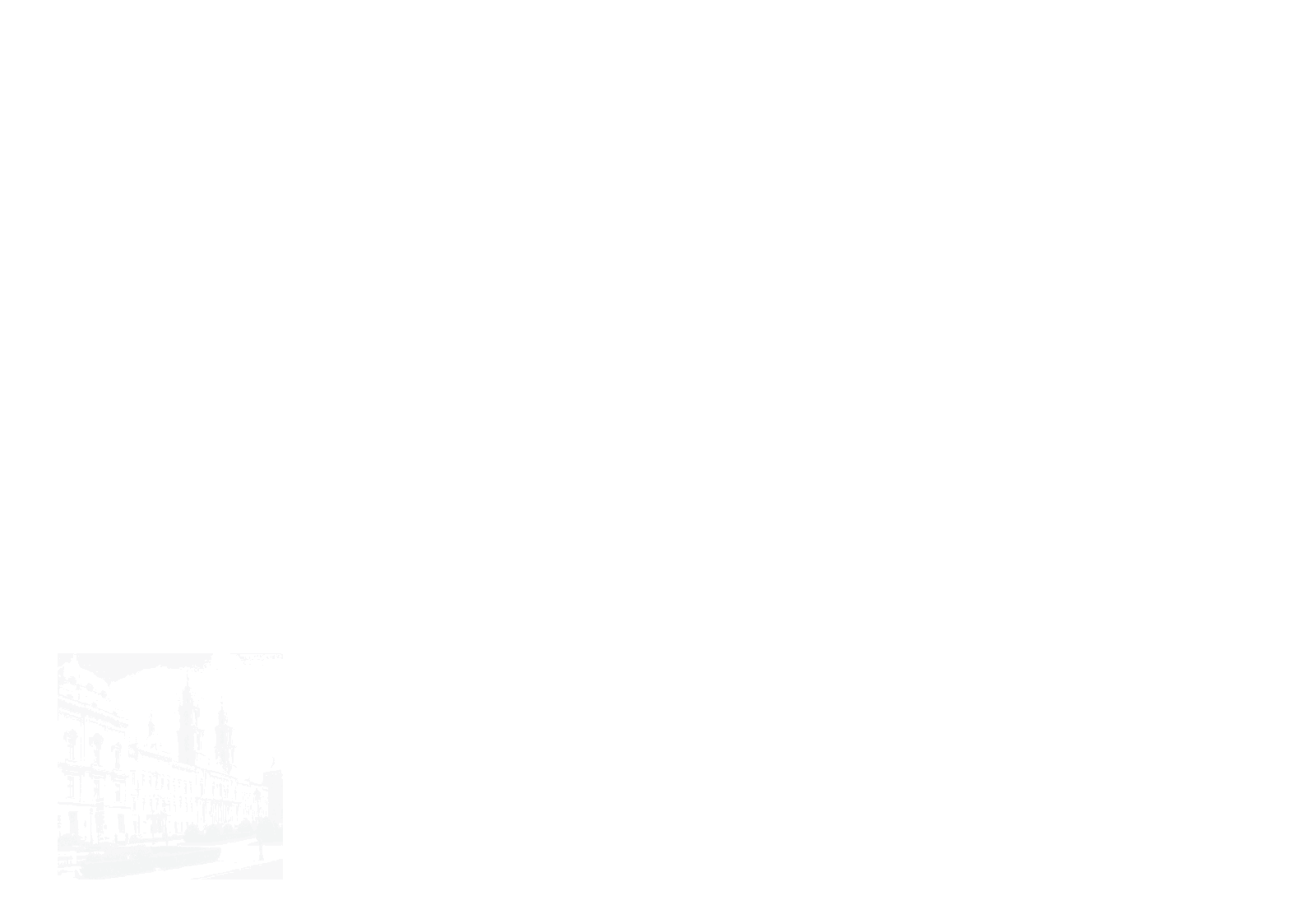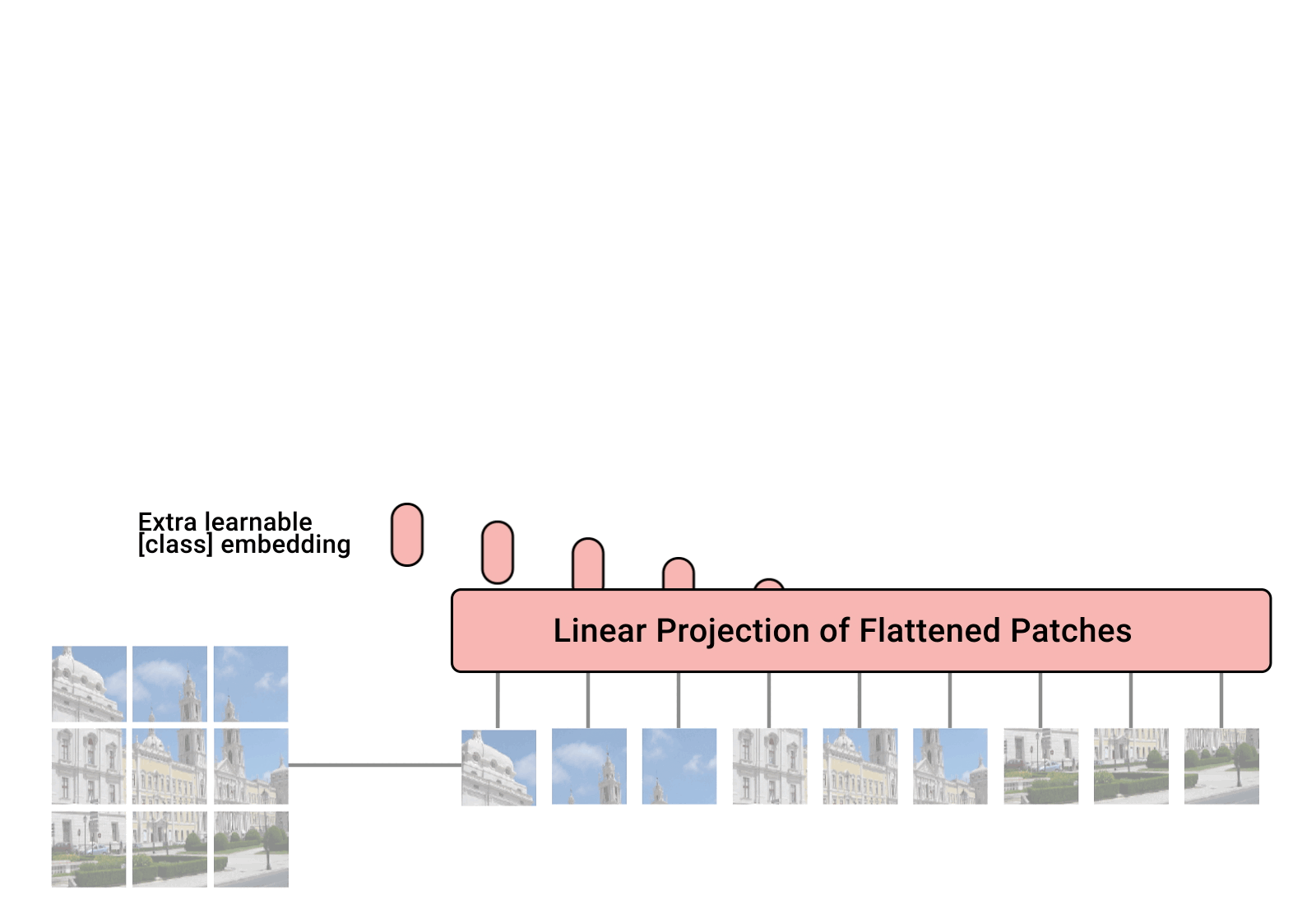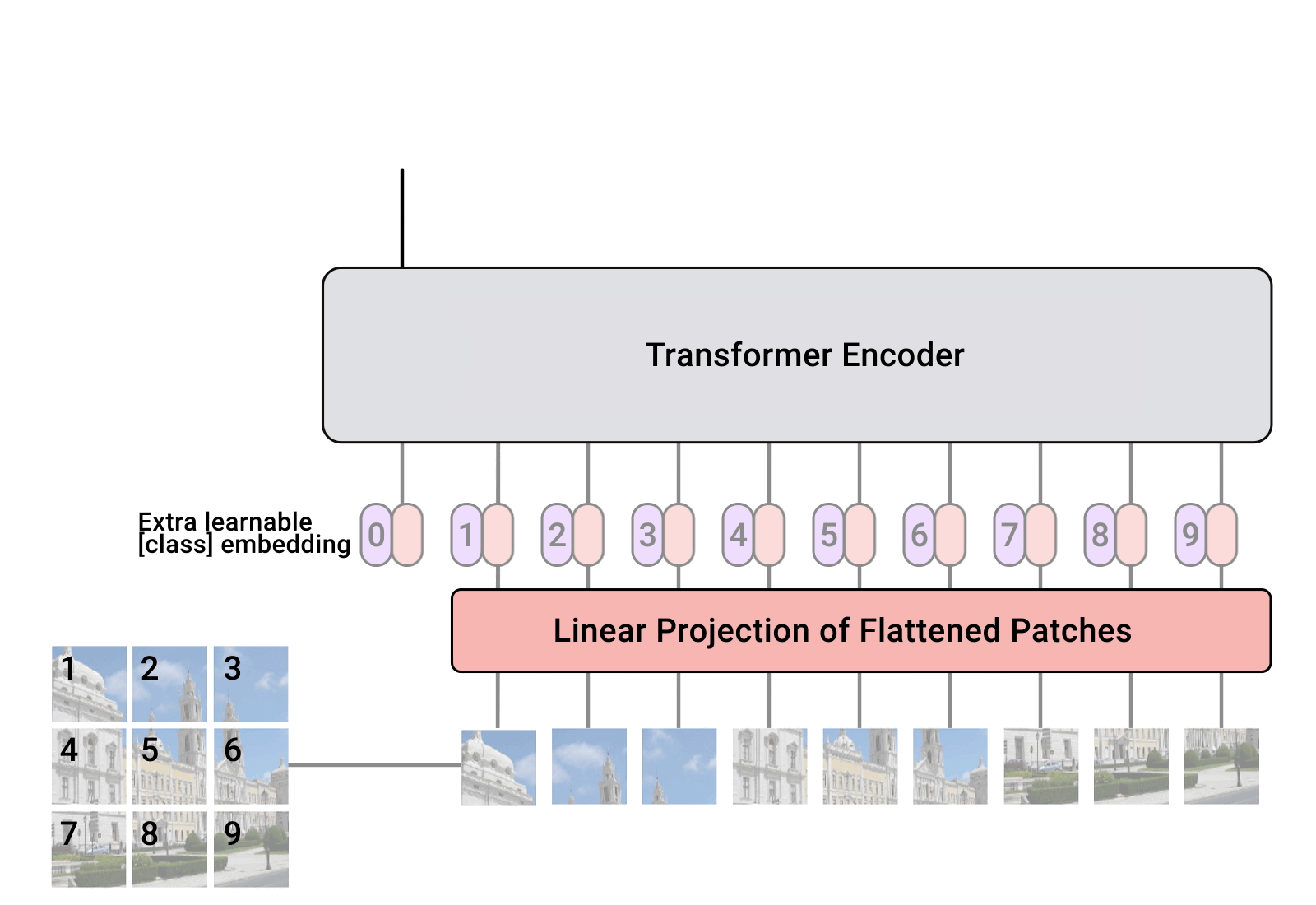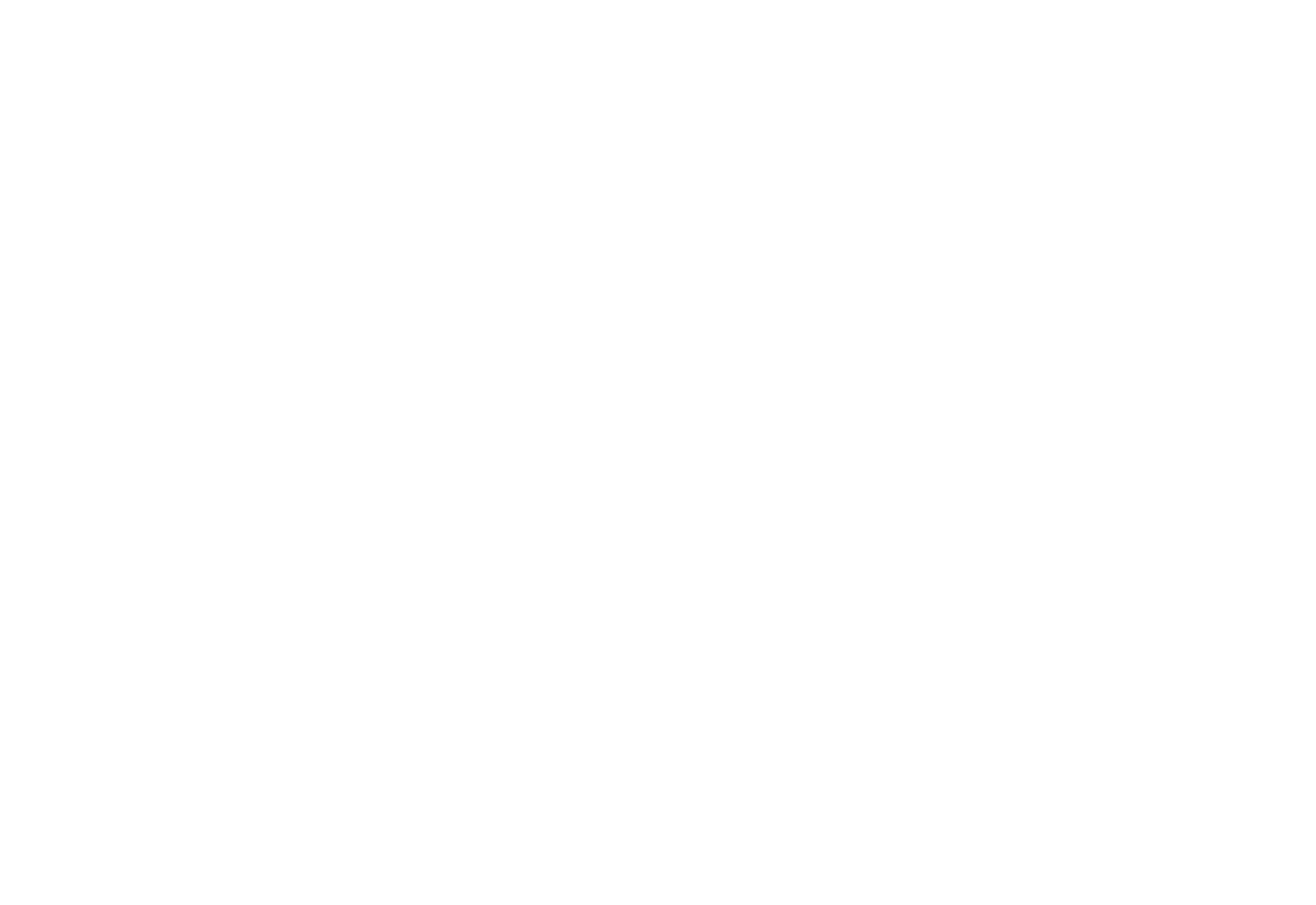
By leveraging these advanced architectures, we can build models that not only understand spatial structures but also learn the temporal dependencies within data, making them ideal for applications like video analysis, human motion tracking, and predictive modeling in dynamic environments.